INTRODUCTION
About this guide
The worldwide payments industry has largely adopted ISO 20022 messaging standards, providing new possibilities to enhance cash management. These standards enable more transparent and consistently structured data-rich information to facilitate greater speed and accuracy.
This guide provides insights on ISO 20022 messaging and how it can improve payments efficiency. We’re also providing personalized support for clients affected by changes. Over time, we will expand capabilities for payments optimization as available via ISO 20022 standards.
SVB’s migration to ISO 20022 is part of our commitment to helping innovation economy businesses succeed and maximize cash management opportunities.

CASH MANAGEMENT BENEFITS OF ISO 20022
ISO 20022 amplifies payments efficiency
As ISO 20022 is adopted globally, companies will be able to realize valuable benefits.
Faster payments
- Enhance cashflow and vendor relationships with more efficient, straight-through processing.
- Increase visibility into liquidity for managing growth.
- Improve compliance by rapidly identifying sanctioned transactions.
Data-rich insights
- Automate compliance reporting using enhanced data and know-your-customer (KYC) protocols.
- Improve fraud detection with rich real-time data for verification and analysis.
- Make data-driven decisions for cash management, CRM, marketing and more.
Flexible & resilient
- Keep pace with change with standards that can adapt to economic changes and emerging technologies.
- Minimize the impact of outages in payment system with efficient re-routing of messages.
MX messages increase efficiency
ISO 20022 MX file types and structured data enable more consistent, detailed messaging for greater payments efficiency compared to legacy formats.
ISO 20022 cash management message types:
- camt.052 – Bank to Customer Account Report. Intraday information that gives a company near real-time visibility into their account(s). The camt.052 replaces the MT942.
- camt.053 – Bank to Customer Statement. Prior-day bank statement with rich, structured detail on all transactions (of all types) posted to the customer’s account the previous day (including cross-border, multiple currency, tax payments, etc.). The camt.053 replaces the MT940, and the message structure includes:
-
- Statement – At least one statement (for each account)
- Balance – Opening and closing balance
- Entry – May be multiple entries
- Entry details – May be multiple details
- Batch
- Transaction details
- camt.054 – Bank to Customer Debit / Credit Notification. Provides specific account debit and credit information for a specific transaction. The camt.054 replaces the MT900 (Confirmation of Debit) and MT910 (Confirmation of Credit) messages.
Greater detail to simplify compliance and reconciliation
- Secure payment tracking. Tracking for all payments, from initiation and clearing, to information reporting, cannot be changed or removed by any party in the payment chain.
- Dedicated purpose code. Specify the reason for the payment from a pre-defined list.
- Dedicated tags for Ultimate Debtor. Increase transparency for payments made on-behalfof others, e.g., factoring or money servicing businesses.
- More data for payer and address information. Can be used throughout the message structure (street name, building number, post code, town name, country, LEI [Legal Entity Identifier]).
Easier to identify sanctioned payments
- Well-organized data. Structured format clearly displays payer data such as name, address, LEI and more to better meet evolving BSA and AML requirements.
- Refined screening. Richer, more consistent data can reduce false positives in sanctions checks.
- Improved compliance. More accurate, data-rich sanctions screening enables companies to more effectively comply with regulations.
Key benefits for teams in your organization
Finance
- Reduce costs with more efficient payment processes.
- Enhance cash management and forecasting with data-rich, real-time reporting.
- Streamline origination and reporting with standardized formats and data.
- Close monthly books faster with enhanced reporting.
Compliance
- Minimize risk by more easily detecting fraud and identifying potential financial crime.
- Simplify compliance with a standard used across multiple payment types.
How ISO 20022 and AI help optimize cash management
The richer structured data in ISO 20022 messaging is ideally suited for unlocking value with AI and machine learning (ML) analysis, including:
- Accelerate insights. Real-time AI analytics can support better decisions for cash allocation and liquidity, spend management, investments, risk reduction and more.
- Lower costs. AI automation and analytics help reduce manual tasks and intervention.
- Reduce fraud risk. Identify anomalies to flag potential fraud or sanctioned transactions.
- Improve forecasting. Analyzing historical data can identify payment patterns to help manage cash flow on the road ahead.
- Boost scalability. As businesses and complexity grow, AI can adapt more seamlessly than traditional cash management processes.
As AI and ISO 20022 adoption are evolving rapidly, companies may need longer-term planning to realize the most benefits.
Use cases that show ISO 20022 benefits
Improve cash management
A growing corporate in the life sciences sector wants to automate delivery of account balance and transaction data for greater visibility into their cash position and to help automate and streamline their payables/receivables processes. Because ISO 20022 is rapidly becoming the go-to universal standard, they can realize new efficiencies while increasing productivity and avoiding the pitfalls of truncated data associated with prior formats. These benefits can be realized using either SVB’s Transact Gateway (TAG) or Swift for Corporates.
Enhance fraud detection
A fintech firm that offers a payments platform needs more streamlined fraud detection to better serve its customers and to stay competitive. With ISO 20022 granular real-time data, they can avoid false positives that may inhibit straight-through processing and keep payments flowing smoothly. The company is also better equipped to stop fraud in its tracks. By preventing costly resolution efforts, they can reduce processing time and risk, saving time and money.
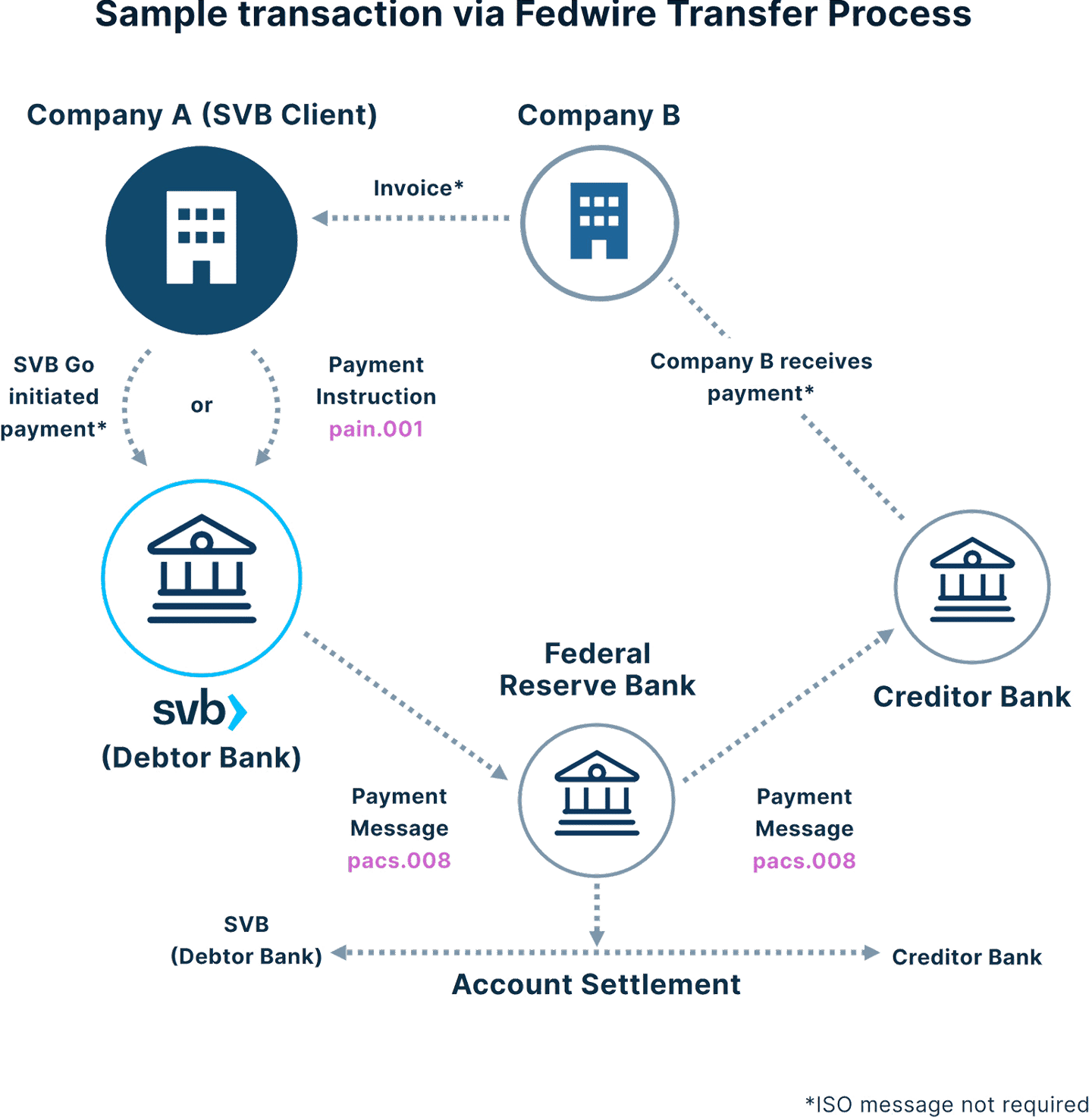
FEDWIRE PAYMENT MESSAGE CHAIN
Message types and parties in a payment message chain: Fedwire Transfer Process Example
In example below, Company B sends invoice to Company A, which initiates the payment process.
SVB SOLUTIONS, ISO 20022 & CASH MANAGEMENT
SVB solutions enhanced for ISO 20022
You can continue to access the SVB payment channels you use today. Channels are evolving with new data fields and enhanced information reporting to provide more opportunities to improve cash management.
If you use any of the services below, we’ll notify you about updating to ISO 20022 with ample time to support you through changes, and will help you get the most benefit.
SVB Go
In SVB Go, you’ll have more options to add new data fields that can help you streamline reconciliation and enhance reporting, although you’ll see little or no changes for daily use. Starting in the third quarter of 2025, you will also have the opportunity to add an end-to-end ID to improve tracking of US domestic payments.
Swift for Corporates
SVB is ready to support new MX message formats for payment initiation (pain.001), while continuing to support legacy MT formats. If you use Swift for Corporates and choose to update from MT formats to ISO 20022 standards, we will proactively notify you with technical specs and ample time to provide support for required changes.
Transact Gateway
Some Transact Gateway (TAG) clients have already made updates to meet ISO compliant formats. We will contact clients using non-compliant formats or who are using non-embedded payment solutions to help prepare, although required changes aren’t due until late 2026.
API Banking
SVB API Banking has wire APIs that are ISO 20022 compliant.
US Domestic Wires (aka Fedwire®) processes have been enhanced to provide new data fields, including: Purpose Code, Related Remittance, Ultimate Debtor (for OBO) and end-to-end ID.
INDUSTRY TIMELINE
SVB migration & client support for ISO 20022
Multi-year effort
Payment networks worldwide are migrating their payment message types to meet the ISO 20022 standards before November 2025, when some key Swift MT payment message formats are discontinued and replaced by ISO 20022 formats.
Since March 2023, SVB has supported both ISO 20022 MX (XML-based) and legacy message formats. We are implementing changes in compliance with industry migration deadlines.
Dedicated client support
For clients affected by the changes, SVB specialists will support you through the transition. You’ll receive timely communications to help you prepare for updates, and we’ll work closely with you to meet ISO 20022 standards and reap the potential benefits.
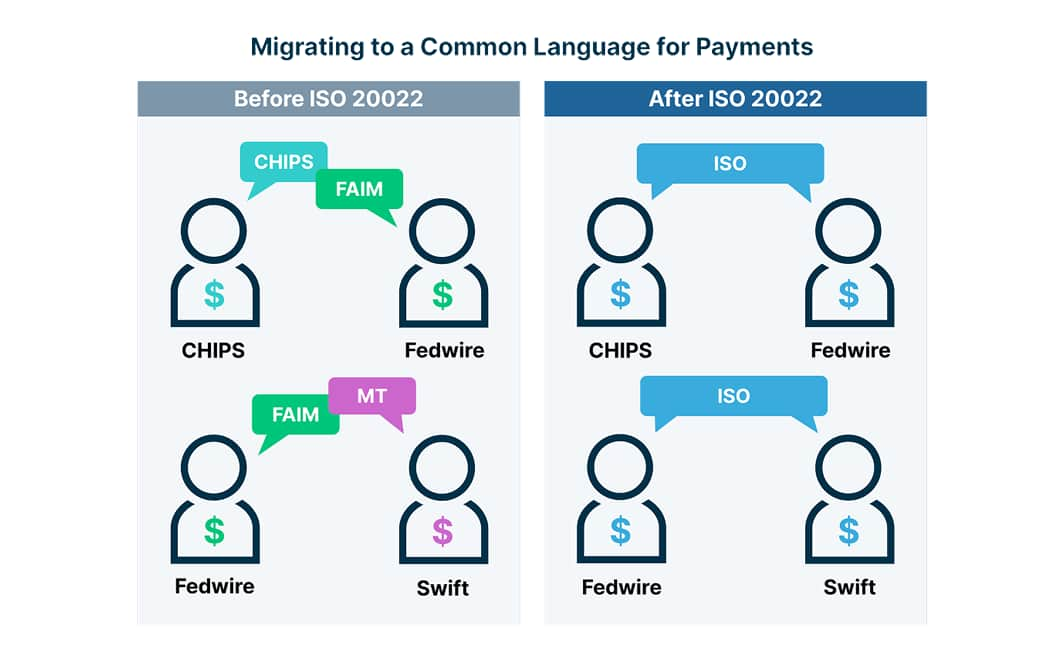
The global evolution of ISO 20022
The International Organization of Standardization (ISO) first introduced the ISO 20022 standards for payments in 2004 and these have evolved over time. Jurisdictions around the world are in the process of adopting the standards to increase global usage. Swift is part of this change, with some of the main transition completing by the end of 2025.
ISO 20022 standards use XML-based messaging formats, file types and data elements to provide a worldwide common language for payment messages.
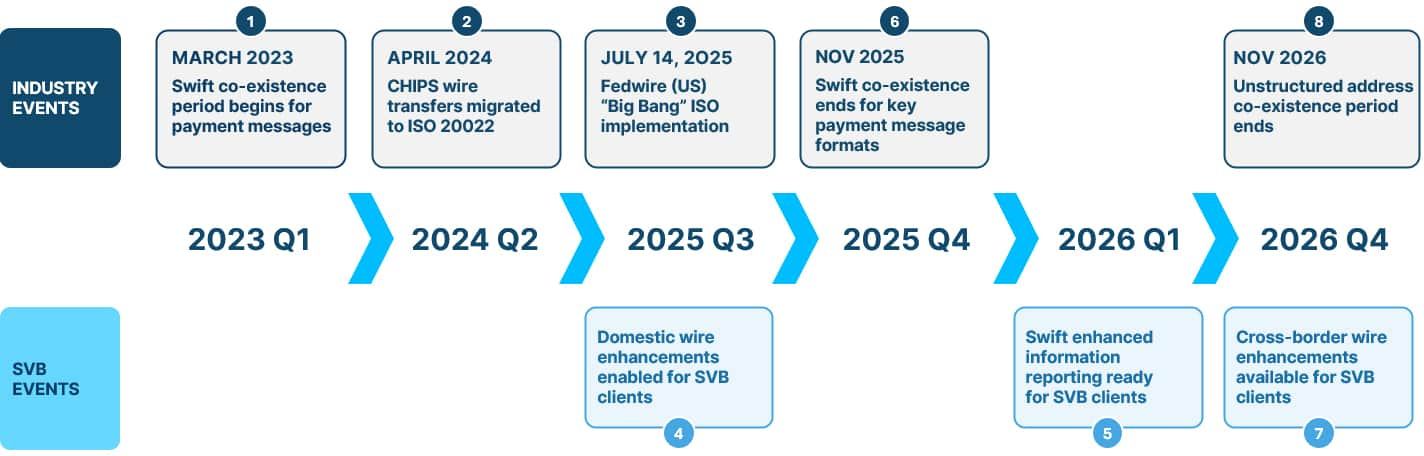
SVB aligns with industry migration dates
To ensure a smooth transition to ISO 20022, we’re working closely with clients and will share details in advance of any changes. Milestones for industry and SVB-specific migration dates:

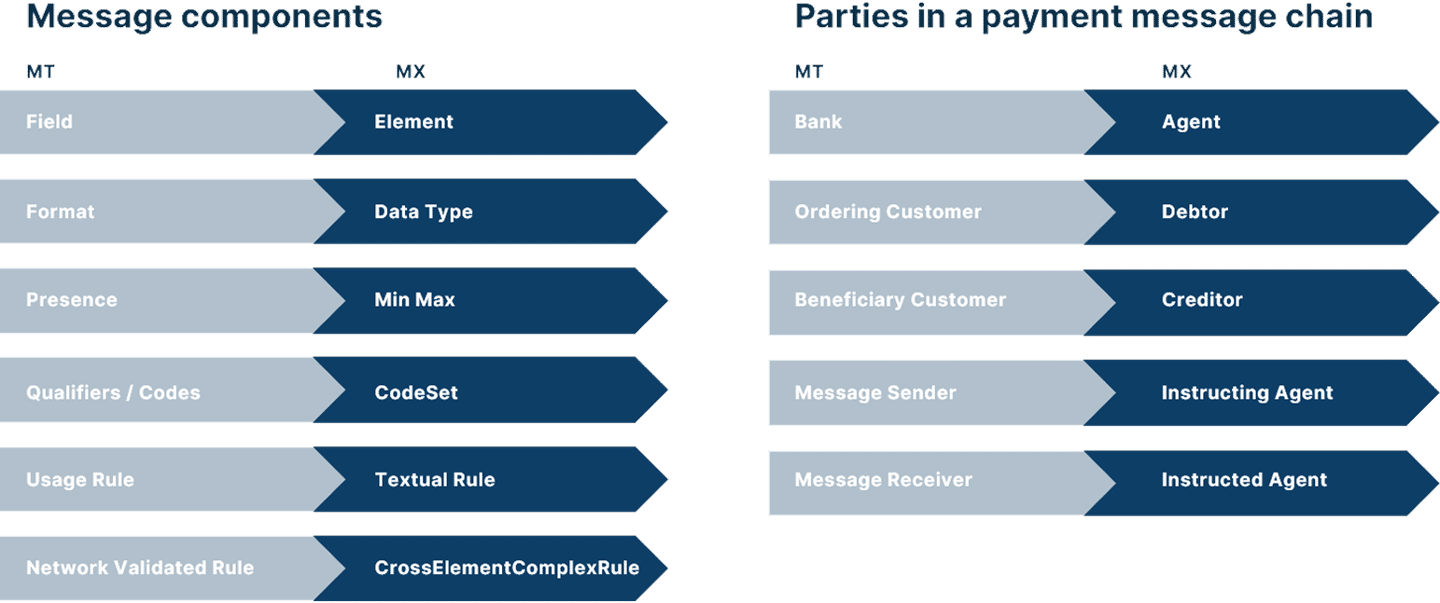
MESSAGE TERMS
ISO messaging terms for payments
- Account owner: Person or entity that legally owns an account and is responsible for transactions in and out of that account.
- Creditor: Person or entity (e.g., vendor, property seller, contractor) that will receive payment for money owed, either via credit transfer initiated by a Debtor, or the Creditor initiates a direct debit payment from the Debtor’s account.
- Debtor: Person or entity that is responsible for making a payment (universal term to refer to payers, buyers, ordering parties, etc.). The Debtor may initiate payment, or the Creditor may initiate a direct debit from the Debtor’s account.
- Initiating party: Debtor or Creditor that initiates a payment, or a party that initiates payment on their behalf.
- Instructed agent: Financial institution that receives payment instructions from the Initiating Party and facilitates money transfer to the end recipient or next agent in the chain. Called an Intermediary Agent in ISO 20022, this entity is used when there’s no direct relationship between the sender’s and receiver’s bank. (In MT files, this was the Message Receiver.)
- Instructing agent: Financial institution that instructs the next party in the payment chain (e.g., Intermediary Agent / Instructed agent) to carry out the payment. (In MT files, this was the Message Sender.)
- Intermediary agent: Financial institution that helps facilitate payment by passing instructions from the Initiating Party to the recipient or next agent in the chain.
- Ultimate Debtor: Person or entity that owes money and is responsible for payment.
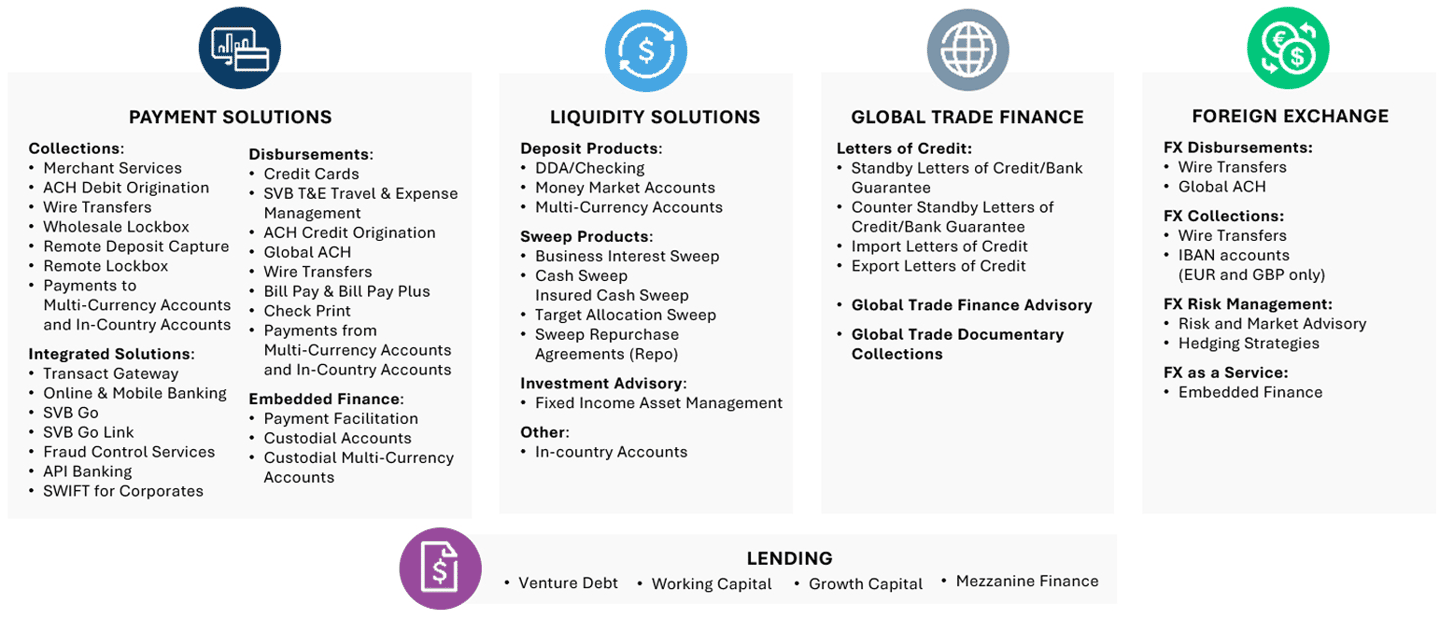
Ecosystem of cash management solutions tailored to your business and stage of growth
Talk with your Relationship Manager about how SVB solutions can help your business.
If you have questions
Please see contact info at the bottom of this page.
ISO 20022 & Swift Services
Information below is included for Swift services users.
MIGRATION DATES
Migration of commonly used message types
Below are anticipated SVB migration timeframes. Information is subject to change. ISO 20022 MX message types not noted below are used less frequently by SVB. If you have questions, please email us at ISOSwiftPaymentQueries@svb.com.
| Message Type | MT | MX | SVB Send/Receive Dates |
| Request for transfer | MT101 | pain.001 | SVB started receiving June 2025 |
| Customer payment status report | N/A | pain.002 | SVB started receiving June 2025 |
| Confirmation of credit/debit | MT900/MT910 | camt.054 | SVB starts sending Q1 2026 |
| External account statements | MT940 | camt.053 | SVB starts sending Q1 2026 |
| Statements (Loro/Vostro & Nostro) | MT950 | camt.053 | SVB starts sending Q1 2026 |
| Interim balance report | MT942 | camt.052 | SVB starts sending Q1 2026 |
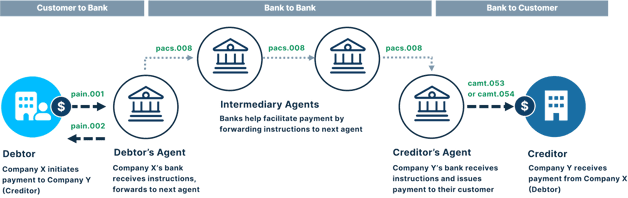
SWIFT FOR CORPORATES PAYMENT EXAMPLE
Swift for Corporates – Credit transfer example
In the example below, the Debtor pays the Creditor using Swift for Corporates via Intermediary Agents. Intermediary Agents act as a bridge to facilitate payments between banks in different countries that don’t have a direct relationship.
Terminology for MX Messages
MESSAGE DATA & TYPES
MT data compared with more highly structured MX data
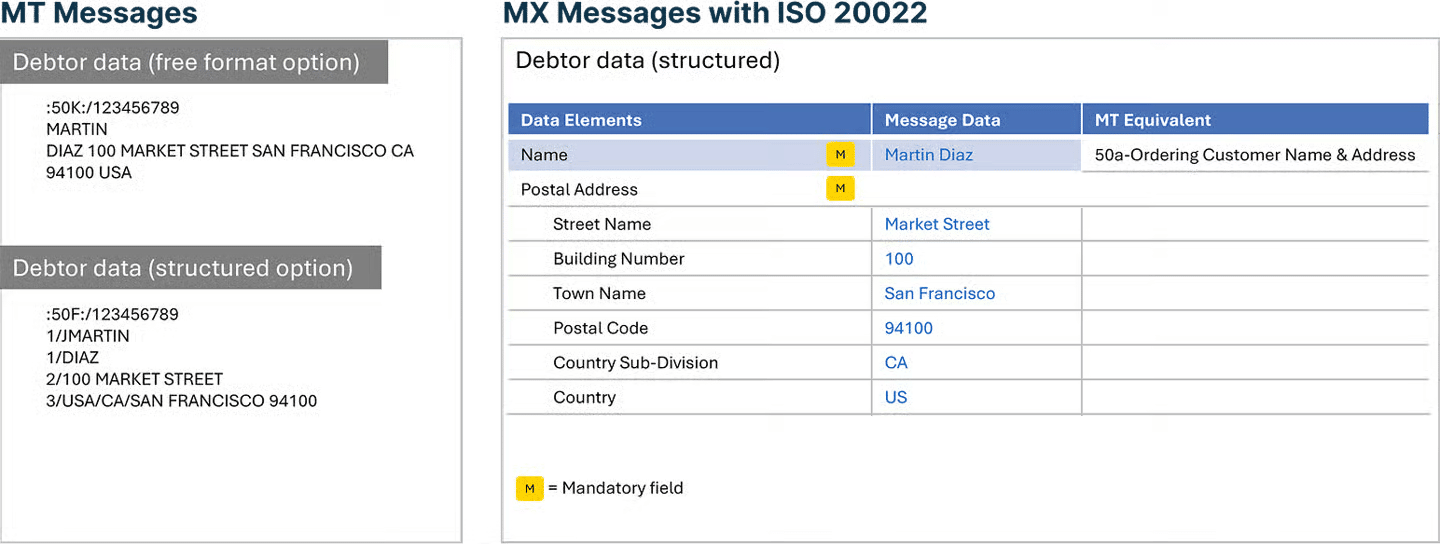
You can see more examples of the MX message structure below on this page.
Select MX message types
| Payment initiation | MT Equivalent | |
| Pain.001 | Payment initiation message between Swift members requesting a customer credit transfer. | MT101 |
| Pain.002 | Payment status message from a bank to the sender of a pain.001 message about status of the initial request (positive, negative, or pending). | None |
| Clearing and settlement | MT Equivalent | |
| Camt.056 | Payment cancellation request. Sent by a bank to the next bank in the chain to try recalling a previously sent pacs.008. Receiving bank responds with a camt.029 and if the response is positive, returns funds via a pacs.004. | MT292/MT992 |
| Pacs.002 | Payment status message from a bank to the sender of a pain.001 message about status of the initial request (positive, negative, or pending). | None |
| Pacs.004 | Payment return. Sent by a bank to the previous bank in the chain to return funds, when the payment debit has already been settled. | None (done previously via MT199 or MT103 marked as return via code word) |
| Pacs.008 | Upon receiving a pain.001 (or similar client payment initiation request), a bank issues an interbank pacs.008 with the payment instruction for the next bank in the chain. | MT103 |
| Pacs.009 | Bank-to-bank message to forward payment instructions. | MT202 |
| Reporting | MT Equivalent | |
| Camt.052 | Intra-day customer account statement. | FIN MT942 |
| Camt.053 | End-of-day customer account statement. | FIN MT940 |
| Camt.054 | Confirmation of credit. Used by the last bank in a payment chain to notify their customer (the Ultimate Creditor) that their account has been credited with a payment. | FIN MT910 |
These are the most commonly used message types for SVB. This is not a complete list.
MX MESSAGE NOMENCLATURE & STRUCTURE
The 4 elements of an ISO 20022 message nomenclature

- Category indicates the core message type
- Type refers to the purpose of the message (e.g., interbank payment instruction)
- Variant and Version indicate updates to the message, such as a status update.
MX message structure overview
Although messages vary in detail, they all follow the same basic format. The list below is an informal categorization of the components of a simple MX message.

MX message structure details
Unique IDs

- ID is in field 20 in MT, and supports only one identifier. In MX, structured data allows differentiation between different IDs, such as separating UETR from the new End-to-End ID field.
- An end-to-end ID is a unique identifier assigned to a payment transaction that makes tracking and reconciliation easier because the ID number remains unchanged across the entire payment process, from initiation to settlement. In contrast, a more general ID number may refer to any identifier used in a specific part of the payment chain and may change during processing, depending on the system involved.
- UETR has 36 characters and is unique to the payment transaction file. It can be traced over the Swift network and used by Swift to provide real time payment status.
Settlement
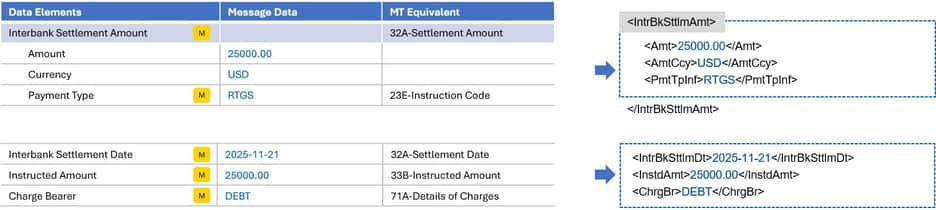
- Amount of money to be moved between the debtor and creditor, before deduction of charges, expressed in the currency as ordered by the initiating party.
- Charge Bearer is the party responsible for covering the costs associated with the processing of this transaction.
Ultimate Debtor/Ultimate Creditor
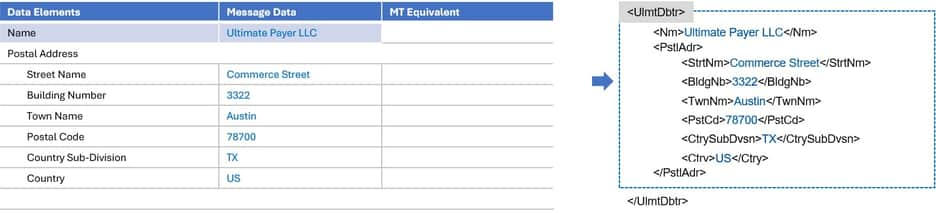
- Ultimate Debtor is the party that ultimately owes the money to the Creditor, even if another party is initiating payment on their behalf. This data field is new for ISO 20022.
- The Debtor field has a similar structure. Debtor is the party who owes an amount of money to the Creditor.
General inquiries
Current SVB clients and partners, please contact your Relationship Manager or your SVB Support Team.
If you do not have a relationship with SVB, you can get started with SVB.
Swift services
Current SVB clients and partners, please reach out to your SVB support team and ask about solution sales.
If you use another partner’s third-party service (e.g., fund administrator) to connect to Swift, please work with that partner directly.
If you do not have a contact at SVB, please email us at ISOSwiftPaymentQueries@svb.com
